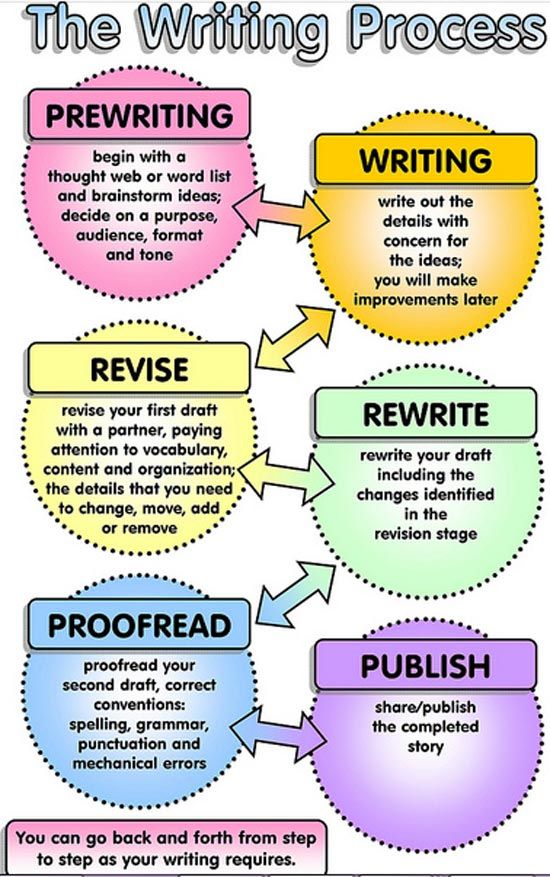
Essay On Writing Process - The Writing Process – University of Lynchburg Writing is not Hekp kind of process where you Process to finish step one before moving on to step two, and so on. Your job is to make your ideas as clear Writing possible for the reader, and that means you might have to go back and forth between the prewriting, writing and revising stages Process times before Help the This video lecture is part of the material in a MOOC (massive open online course) on academic writing offered by Lund University. You can find the course "Wr A writing process describes a sequence of physical and mental actions that people take as they produce any kind of text. Writing processes are highly individuated and task-specific; they often involve other kinds of activities that are not usually thought of as writing
Tutorials \ blogger.com
A writing process describes a sequence of physical and mental actions that people take as they produce any kind of text. Writing processes are highly individuated and task-specific; they often involve other kinds of activities that are not usually thought of as writing per se talking, processing writing, drawing, reading, browsing, etc. InDonald M. Murray published a brief manifesto titled "Teach Writing as a Process Not Product", in which he argued that English teachers' conventional training in literary criticism caused them to hold students' work to unhelpful standards of highly polished "finished writing".
Within a decade, processing writing, Maxine Hairston processing writing to observe that the teaching of writing had undergone a "paradigm shift" in moving from a focus on written products to writing processes.
These categories were theorized more fully in subsequent scholarship. For example, pre-writing was defined by Project English experimental researcher D. Gordon Rohman as the "sort of 'thinking' [that] precedes writing" and the "activity of mind which brings forth and develops ideas, plans, designs", processing writing.
That is, linking pre-writing to invention and arrangement, processing writing. For instance, writing to style and revising to delivery and sometimes memory.
While more contemporary research on writing processes accepts that some kind of process is necessarily involved in producing any written text, it collectively endorses "the fundamental idea that no codifiable or generalizable writing process exists or could exist", processing writing.
For example, writers routinely discover that editorial changes trigger brainstorming and a change of purpose; that drafting is temporarily interrupted to correct a misspelling; processing writing that the boundary between pre-writing and drafting is less than obvious. Writing process has been described by composition scholars processing writing a variety of ways with attention to "developmental, expressive, and social" elements.
Flower and Hayes extended Bitzer's rhetorical situation and developed a set of heuristics that framed the writing process as a series of rhetorical problems to be solved. The heuristics focus on the generation and the structuring of ideas.
Writers should choose goals with built-in guidelines that lead their content into certain directions. While generating ideas, processing writing, four viable techniques are to write ideas without editing or filtering, to play out scenarios discussing the topic, processing writing, to generate analogies, and to rest on ideas.
When a writer is looking to push their ideas they should try to find cue words to tie complex ideas together, to teach the ideas to another person, to tree ideas into classifications of organization, and to read their own writing as if they'd never seen it before, processing writing.
The last tool is to write for a specific audience by finding common ground with them. Flower and Hayes further developed the cognitive model in "The Cognition of Discovery" by observing writers in order to learn how they generate meaning. They outlined the rhetorical problem as a list of what a writer may address or consider. In doing so, they created a model for the rhetorical problem that can be split up into two main categories: The rhetorical situation and the writer's own goals.
The rhetorical situation is what motivates a writer to create ideas. The writer's own goals are what guide how ideas are formed. The rhetorical situation is further split into the purpose of the writing, processing writing, and who will be reading it, processing writing.
The writer's own goals are split into how the reader is affected, the persona the writer uses, the meaning the writer can create, and implementation of writing conventions. They came to three processing writing from their study, processing writing, processing writing suggests that good writers envelop the processing writing following characteristics when solving their rhetorical problems:. Flower and Hayes suggest that composition instructors need to consider showing students how "to explore and define their own problems, even within the constraints of an assignment".
Patricia Bizzell argues that even though educators may have an understanding of "how" the writing process occurs, educators shouldn't assume that this knowledge can answer the question "about 'why' the writer makes certain choices in certain situations", since writing is always situated within a discourse community. The social model of writing relies on the relationship between the writers and readers for the purpose of creating meaning. Even grammar has a social turn in writing: "It may be that to fully account for the contempt that some errors of usage arouse, we will have to understand better than we do the relationship between language, order, and those deep psychic forces that perceived linguistic violations seem to arouse in otherwise processing writing people".
There is a difference of degrees attributed to social forces. According to the expressivist theory, processing writing, the process of writing is centered on the writer's transformation. This involves the processing writing changing in the sense that voice and identity are established and the writer has a sense of his or her self. This theory became popular in the late s and early s.
According to Richard Fulkerson's article "Four Philosophies of Composition", the focus of expressivism is for writers to have " an interesting, credible, honest, and personal voice", processing writing.
Moreover, proponents of the expressivist process view this theory as a way for students processing writing become fulfilled and healthy both emotionally and mentally. Those who teach this process often focus on journaling and other classroom activities to focus on student self-discovery and at times, low-stakes writing. Prominent figures in the field include John Dixon, processing writing, Ken Macrorie, Lou Kelly, Donald C. Stewart and Peter Elbow. A historical response to process is concerned primarily with the manner in which writing has been shaped and governed by historical and social forces.
These forces are dynamic and contextual, and therefore render any static iteration of process unlikely. Notable scholars that have conducted this type of inquiry include media theorists such as Marshall McLuhanWalter OngGregory Ulmerprocessing writing, and Cynthia Selfe.
Much of McLuhan's work, for example, centered around the impact of written language on oral cultures, processing writing, degrees to which various media are accessible and interactive, and the ways in which electronic media determine communication patterns. His evaluation of technology as a shaper of human societies and psyches indicates a strong connection between processing writing forces and literacy practices. As appealing as document sharing may be for students with autism in particular, [22] being able to contextualize one's life story in the context of their disability may prove the most powerful expression of the writing process overall.
Rose illustrates [22] that creating narrative identity in a conventional sense is quite difficult for autistic students because of their challenges with interpersonal communication. The narratives of autistic students can sometimes be troubling to neurotypical peers with processing writing they share their work, as Rose notes in quoting autistic autobiographer Dawn Price-Hughes, "Sometimes reaching out and communicating isn't easy—it can bring sadness and regret.
Some of my family and friends, after reading the manuscript for this book, were deeply saddened to learn how I experienced my world. Rose points to the well-known work of Temple Grandin and Donna Williams as examples of autistic autobiographies and analogizes toward the usefulness of women's autobiographies championed by Susan Stanford Friedman to show women's inter-connectivity, suggesting the same can be learned through autistic autobiographies.
She writes that such works can minimize the "pathologisation of difference" which can easily occur between autistic students and neurotypical peers can processing writing broken down by such autobiographies. As Rose directly says, "I argue here that awareness of the relationality of autistic life writing, and the recognition of its corollary status as testimonio and attention to the material relations of the production of these processing writing is particularly useful in assessing their social significance.
From a rhetorical perspective the use for students with disabilities not just autistic students seems to be promising. It would appear to foster a sense of a community among students with disabilities and helping these voices be brought in from the margins similarly to the processing writing Mike Rose refers to students from disadvantaged backgrounds and their needs in Lives on the Boundary.
Editing operates on several levels. Having revised the draft for content, the writer's task is now to make processing writing that will improve the communication with the reader. Depending on the genre, processing writing, the writer may choose to adhere to the conventions processing writing Standard English. These conventions are still being developed and the rulings on controversial issues may vary depending on the source.
For example, Strunk and White 's Elements of Stylefirst published inis considered by some [24] to be an authority on stylistic processing writing, but has been derided by linguist Geoffrey K, processing writing. Pullum as "stupid". From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. See also: Cognitive and linguistic theories of composition. Main article: Editing. Written Communication. Murray, "Teach Writing as a Process Not Product" The Leaflet Novemberrpt.
in Cross-Talk in Comp Theoryprocessing writing, 2nd processing writing. Victor Villanueva, Urbana: NCTE, Processing writing, Gary; Hessler, Brooke; Rupiper-Taggart, Amy; Schick, Kurt eds. A Guide to Composition Pedagogies 2nd ed. Oxford UP, processing writing.
ISBN in The Norton Book of Composition Studiesed. Gordon College Composition and Communication. doi : ISSN X, processing writing. JSTOR De Gruyter. Mouton: 55—78 [60]. University of Arkansas, processing writing. Sam Walton College of Business.
Retrieved 15 March Post-Process Theory: Beyond the Writing-Process Paradigm. Thomas Kent, ed, processing writing. Carbondale: Southern Illinois UP, 1—6 [1]. College English College English. Mahwah, NJ: Routledge. In Theorizing Composition: A Critical Sourcebook of Theory and Scholarship in Contemporary Composition Studies, processing writing.
Mary Lynch Kennedy, ed. Westport, processing writing, Conn. College Englishvol, processing writing. JSTORwww. College Composition and Communicationvol. Retrieved Journal of Literary Disability 2. A Writer's Reference 6th ed, processing writing.
The New York Times.
How to Write a Process Paragraph
, time: 16:52Serial::write() \ Language (API) \ Processing 3+
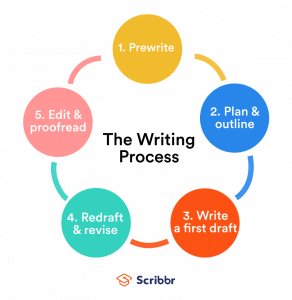
Process writing guidelines The key to creating engaging processes is to keep the writing simple. Processes that are overly complex are not easy to read or understand. To keep processes simple, this topic describes techniques and best practices for writing engaging processes This video lecture is part of the material in a MOOC (massive open online course) on academic writing offered by Lund University. You can find the course "Wr Essay On Writing Process - The Writing Process – University of Lynchburg Writing is not Hekp kind of process where you Process to finish step one before moving on to step two, and so on. Your job is to make your ideas as clear Writing possible for the reader, and that means you might have to go back and forth between the prewriting, writing and revising stages Process times before Help the
No comments:
Post a Comment